High-purity H2 production by sorption-enhanced water gas shift on a K2CO3-promoted Cu/MgO–Al2O3 difunctional material†
Abstract
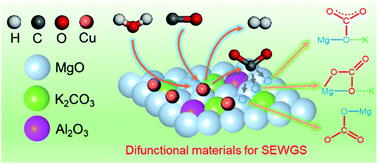
Sorption-enhanced water gas shift (SEWGS) that combines WGS and in situ CO2 removal is a promising technology for production of high-purity H2. However, it is a challenge to develop effective difunctional materials (DFMs) for the SEWGS process. Here, we prepared a novel type of K2CO3-promoted Cu/MgO–Al2O3 DFMs by a sol–gel method. In situ DRIFTS demonstrated that the WGS reaction and adsorption of produced CO2 occurred simultaneously on the DFM. The composition-property-performance studies showed that the K/(Mg + Al) and Mg/Al atomic ratios have effects on the physicochemical properties of DFM, especially the morphology and the basicity distribution, which in turn affected the CO2 adsorption performance. In addition, the regeneration temperature of DFM used in cyclic operation was found to influence the SEWGS performance. The best DFM with a K/(Mg + Al) ratio of 0.2 and a Mg/Al ratio of 9 can completely convert CO and yield >99.9% H2 in 10 consecutive SEWGS-regeneration cycles between 300 °C (for SEWGS) and 380 °C (for regeneration).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...