Pencil graphite rods decorated with nickel and nickel–iron as low-cost oxygen evolution reaction electrodes†
Abstract
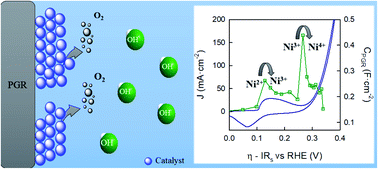
Society is demanding clean energy to substitute greatly polluting carbon-based fuels. As an alternative, the use of green hydrogen produced by electrocatalysis constitutes a nice strategy as its products and reactants are not toxic to the environment. However, the use of scarce materials and high overpotentials to accomplish the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) make electrocatalysis an uncompetitive process. To solve these challenges, a low-cost procedure for the preparation of earth-abundant Ni, Fe and NiFe decorated electrodes has been developed. For this purpose, pencil graphite rods have been selected as highly porous substrates. A reasonable performance is achieved when they are employed for the OER. Furthermore, for the first time, a detailed analysis of impedance spectroscopy allows the association of the Ni redox transitions Ni2+/Ni3+ and Ni3+/Ni4+ (including the identification of the hydrated α–γ and the non-hydrated β phases) with an electrochemical redox capacitance response. Additionally, the Ni3+/Ni4+ redox peak capacitance together with a quick decrease in the charge transfer resistance indicates the implication of Ni4+ in the OER. These results show the utility of impedance spectroscopy as a non-destructive and non-invasive technique to study these electrochemical systems in detail under operating conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...