Thermoelectric all-carbon heterostructures for a flexible thermoelectric generator†
Abstract
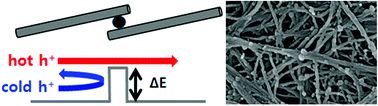
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are thermoelectric materials with immense potential because of their flexible, lightweight, and solution-processable properties. Herein, we report a facile method for improving the thermoelectric performance of CNTs for application in flexible thermoelectric generators. By introducing carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) between the CNTs, all-carbon heterostructures could be formed. A barrier energy at the CNT–CNP interface can directly enhance the Seebeck coefficient (S). The all-carbon heterostructure films exhibited S and power factor values as high 54.0 ± 1.4 μV K−1 and 503 ± 49 μW m−1 K−2, respectively, which are 1.9 and 2.3 times higher than those of the CNT films without the heterostructures. Note that the thermoelectric performance is considered only from the point of view of the power factor. For complete characterization, the evaluation of thermal conductivity would be required. Using the all-carbon heterostructures as thermoelectric elements, a flexible thermoelectric generator of three-dimensionally stacked elements was fabricated for efficiently harvesting energy from a vertical temperature difference. The thermoelectric generator with a thermal contact area of 6 cm2 exhibited a maximum output power of 4.8 μW from a vertical temperature difference of 30 K. Thus, we developed a facile strategy for synthesizing high-performance thermoelectric all-carbon heterostructures and demonstrated their superior ability to harvest thermoelectric energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...