MXenes: promising donor and acceptor materials for high-efficiency heterostructure solar cells†
Abstract
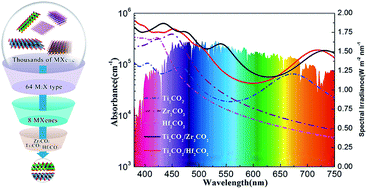
Constructing heterostructure solar cells using donor and acceptor semiconductors has attracted global interest owing to their high power conversion efficiency. In this paper, based on density functional theory calculations, we comprehensively evaluated 64 two-dimensional transition metal carbides (MXenes) to explore them as appropriate semiconductors for solar cells by material screening. The results highlight that Zr2CO2 (Hf2CO2) and Ti2CO2 are promising donor and acceptor materials, respectively. Interestingly, the heterostructures have a moderate band gap of 1.22 eV and exhibit a noticeable absorbance coefficient of 105 cm−1 in the visible light region. Moreover, the type-II nature of the heterostructures could induce effective electron–hole separation. Furthermore, the photocurrents of Ti2CO2/Zr2CO2 and Ti2CO2/Hf2CO2 heterostructure solar cell devices are competitive with those of silicon devices. In particular, Ti2CO2/Zr2CO2 and Ti2CO2/Hf2CO2 heterostructure solar cells deliver a very high power conversion efficiency of 22.74% and 19.56%, respectively. Our present study paves the way for facilitating the potential application of MXenes as photovoltaic materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...