Abstract
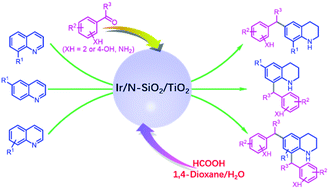
The incorporation of a coupling step into the reduction of unsaturated systems offers a desirable way for diverse synthesis of functional molecules, but it remains to date a challenge due to the difficulty in controlling the chemoselectivity. Herein, by developing a new heterogeneous iridium catalyst composed of Ir-species (Irδ+) and N-doped SiO2/TiO2 support (Ir/N-SiO2/TiO2), we describe its application in reductive electrophilic mono and dialkylations of quinolines with various 2- or 4-functionalized aryl carbonyls or benzyl alcohols by utilizing renewable formic acid as the reductant. This catalytic transformation offers a practical platform for direct access to a vast range of alkyl THQs, proceeding with excellent step and atom-efficiency, good substrate scope and functional group tolerance, a reusable catalyst and abundantly available feedstocks, and generation of water and carbon dioxide as by-products. The work opens a door to further develop more useful organic transformations under heterogeneous reductive catalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...