A molecular twist on hydrophobicity†
Abstract
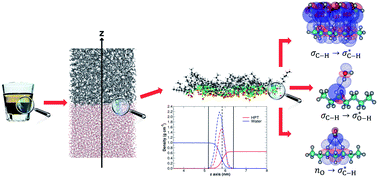
A thorough exploration of the molecular basis for hydrophobicity with a comprehensive set of theoretical tools and an extensive set of organic solvent S/water binary systems is discussed in this work. Without a single exception, regardless of the nature or structure of S, all quantum descriptors of bonding yield stabilizing S⋯water interactions, therefore, there is no evidence of repulsion and thus no reason for etymological hydrophobicity at the molecular level. Our results provide molecular insight behind the exclusion of S molecules by water, customarily invoked to explain phase separation and the formation of interfaces, in favor of a complex interplay between entropic, enthalpic, and dynamic factors. S⋯water interfaces are not just thin films separating the two phases; instead, they are non-isotropic regions with density gradients for each component whose macroscopic stability is provided by a large number of very weak dihydrogen contacts. We offer a definition of interface as the region in which the density of the components in the A/B binary system is not constant. At a fundamental level, our results contribute to better current understanding of hydrophobicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...