Highly efficient Lewis acid catalytic activity of the tritylium ion at the node of a tensile organic framework†
Abstract
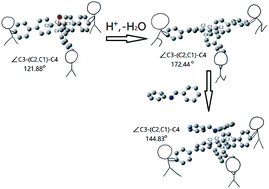
Tritylium salts have been used as Lewis acid catalysts in organic synthesis for a long time. In this work, we found that the Lewis acid catalytic activity of tritylium ions at the node of a tensile framework is significantly improved compared to that of the free tritylium salts. The tritylium-based framework, PAF-201 (PAF, porous aromatic framework), was prepared by acidification of a semi-rigid triphenylcarbinol-based parent framework, PAF-200. When PAF-200 was alternately exposed to HCl and NH3 gas, a fast allochroic cycle was observed due to repeated formation of tritylium species. Interestingly, the pseudo-first-order reaction rate of a Povarov model reaction catalyzed by PAF-201 as a Lewis acid was ∼3.7 times and ∼4.7 times as those of tritylium tetrafluoroborate and tri(4-biphenyl)carbonium tetrafluoroborate, respectively. Theoretical calculations revealed that the tritylium ion at the node of PAF-201 has a quasi-planar structure. The transformation of triphenylcarbinol in PAF-200 to tritylium in PAF-201 can make the framework taut, and the rebounding force toward the tetrahedral structure is stored. This is favorable for tritylium to activate the imine substrate along with a deformation of the quasi-plane to tetrahedron. PAF-201 could be easily recycled at least three times without evident loss of catalytic activity. This work presents the catalytic activity of the tritylium ion under stress.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...