Vibrational exciton delocalization precludes the use of infrared intensities as proxies for surfactant accumulation on aqueous surfaces†
Abstract
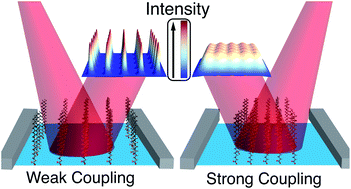
Surface-sensitive vibrational spectroscopy is a common tool for measuring molecular organization and intermolecular interactions at interfaces. Peak intensity ratios are typically used to extract molecular information from one-dimensional spectra but vibrational coupling between surfactant molecules can manifest as signal depletion in one-dimensional spectra. Through a combination of experiment and theory, we demonstrate the emergence of vibrational exciton delocalization in infrared reflection–absorption spectra of soluble and insoluble surfactants at the air/water interface. Vibrational coupling causes a significant decrease in peak intensities corresponding to C–F vibrational modes of perfluorooctanoic acid molecules. Vibrational excitons also form between arachidic acid surfactants within a compressed monolayer, manifesting as signal reduction of C–H stretching modes. Ionic composition of the aqueous phase impacts surfactant intermolecular distance, thereby modulating vibrational coupling strength between surfactants. Our results serve as a cautionary tale against employing alkyl and fluoroalkyl vibrational peak intensities as proxies for concentration, although such analysis is ubiquitous in interface science.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Chemical Science HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...