Total synthesis, isolation, surfactant properties, and biological evaluation of ananatosides and related macrodilactone-containing rhamnolipids†
Abstract
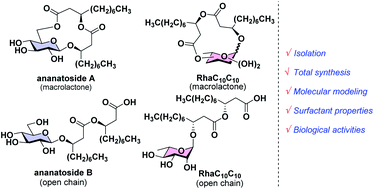
Rhamnolipids are a specific class of microbial surfactants, which hold great biotechnological and therapeutic potential. However, their exploitation at the industrial level is hampered because they are mainly produced by the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The non-human pathogenic bacterium Pantoea ananatis is an alternative producer of rhamnolipid-like metabolites containing glucose instead of rhamnose residues. Herein, we present the isolation, structural characterization, and total synthesis of ananatoside A, a 15-membered macrodilactone-containing glucolipid, and ananatoside B, its open-chain congener, from organic extracts of P. ananatis. Ananatoside A was synthesized through three alternative pathways involving either an intramolecular glycosylation, a chemical macrolactonization or a direct enzymatic transformation from ananatoside B. A series of diasteroisomerically pure (1→2), (1→3), and (1→4)-macrolactonized rhamnolipids were also synthesized through intramolecular glycosylation and their anomeric configurations as well as ring conformations were solved using molecular modeling in tandem with NMR studies. We show that ananatoside B is a more potent surfactant than its macrolide counterpart. We present evidence that macrolactonization of rhamnolipids enhances their cytotoxic and hemolytic potential, pointing towards a mechanism involving the formation of pores into the lipidic cell membrane. Lastly, we demonstrate that ananatoside A and ananatoside B as well as synthetic macrolactonized rhamnolipids can be perceived by the plant immune system, and that this sensing is more pronounced for a macrolide featuring a rhamnose moiety in its native 1C4 conformation. Altogether our results suggest that macrolactonization of glycolipids can dramatically interfere with their surfactant properties and biological activity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Most popular 2021 chemical biology articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...