Expanding the scope of native chemical ligation – templated small molecule drug synthesis via benzanilide formation†
Abstract
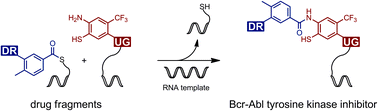
We describe a reaction system that enables the synthesis of Bcr–Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) via benzanilide formation in water. The reaction is based on native chemical ligation (NCL). In contrast to previous applications, we used the NCL chemistry to establish aromatic rather than aliphatic amide bonds in coupling reactions between benzoyl and o-mercaptoaniline fragments. The method was applied for the synthesis of thiolated ponatinib and GZD824 derivatives. Acid treatment provided benzothiazole structures, which opens opportunities for diversification. Thiolation affected the affinity for Abl1 kinase only moderately. Of note, a ponatinib-derived benzothiazole also showed nanomolar affinity. NCL-enabled benzanilide formation may prove useful for fragment-based drug discovery. To show that benzanilide synthesis can be put under the control of a template, we connected the benzoyl and o-mercaptoaniline fragments to DNA and peptide nucleic acid (PNA) oligomers. Complementary RNA templates enabled adjacent binding of reactive conjugates triggering a rapid benzoyl transfer from a thioester-linked DNA conjugate to an o-mercaptoaniline-DNA or -PNA conjugate. We evaluated the influence of linker length and unpaired spacer nucleotides within the RNA template on the product yield. The data suggest that nucleic acid-templated benzanilide formation could find application in the establishment of DNA-encoded combinatorial libraries (DEL).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...