Ultrasensitive small molecule fluorogenic probe for human heparanase†
Abstract
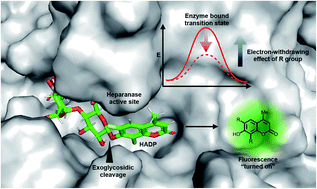
Heparanase (HPA) is a critical enzyme involved in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and its elevated expression has been linked with diseases such as various types of cancer and inflammation. The detection of heparanase enzymatic activity holds tremendous value in the study of the cellular microenvironment, and search of molecular therapeutics targeting heparanase, however, no structurally defined probes are available for the detection of heparanase activity. Here we present the development of the first ultrasensitive fluorogenic small-molecule probe for heparanase enzymatic activity via tuning the electronic effect of the substrate. The probe exhibits a 756-fold fluorescence turn-on response in the presence of human heparanase, allowing one-step detection of heparanase activity in real-time with a picomolar detection limit. The high sensitivity and robustness of the probe are exemplified in a high-throughput screening assay for heparanase inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...