Green, scalable, low cost and reproducible flow synthesis of biocompatible PEG-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
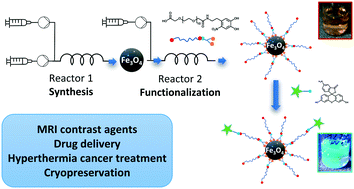
Functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles are of great interest for multiple biomedical applications. However, it remains a considerable challenge to manufacture these nanoparticles reproducibly on a large scale with the appropriate surface coating to render them completely stable and biocompatible. To overcome this problem, a novel combination of synthesis and functionalization using modular microreactor systems is presented here, avoiding the need of intermediate ligand exchange steps. Continuous flow technology enables reproducible synthesis of bare iron oxide nanoparticles (7 ± 2 nm) in water under mild conditions, in tandem with extremely fast and efficient functionalization with a custom heterobifunctional PEG stabilizer. The nanoparticles can be easily derivatized with any molecule of interest through simple amide coupling, demonstrating their capacity to act as a versatile platform for biomedical applications. The produced iron oxide nanoparticles are fully biocompatible based on a LDH cytotoxicity assay, highly stable in various biologically relevant media and suitable for T2 MRI contrast applications (r1 = 1.44 mM−1 s−1, r2 = 272 mM−1 s−1). A full cost analysis reveals the commercial viability of the process, with a total cost as low as £ 506 g−1, demonstrating the potential of this modular approach to enable the large-scale deployment of functionalized nanomaterials in real world applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...