Continuous-flow diazotization of red base KD hydrochloride suspensions in a microreaction system†
Abstract
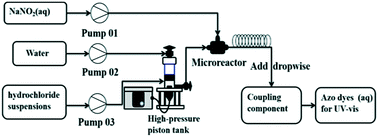
In this work, a continuous-flow microreaction system has been developed to perform the diazotization reaction of red base KD hydrochloride in the form of a suspension solution. By investigating the effects of reaction temperature, reactant volume flow, red base KD concentration and reaction time on the diazotization reaction, the optimal reaction conditions were obtained. According to the solid–liquid reaction model, we found that the agglomeration of suspensions significantly affects the diazotization reaction due to the solid–liquid mass transfer process. Consequently, different red base KD hydrochloride suspensions were prepared under different conditions to explore the agglomeration phenomenon of the suspensions, and we observed that the crystal agglomeration could be prevented by optimizing the process of preparing the reaction suspensions. The results showed that the yield of the diazotization reaction using these optimized suspensions, which were prepared by introducing concentrated hydrochloric acid in three sequential additions of equal volume, could reach over 99% in 21.2 s at two different suspension concentrations (suspension concentration: 0.12 mol L−1 and 0.15 mol L−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...