Fly ash-, foundry sand-, clay-, and pumice-based metal oxide nanocomposites as green photocatalysts
Abstract
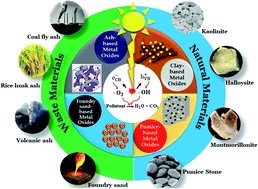
Metal oxides possess exceptional physicochemical properties which make them ideal materials for critical photocatalytic applications. However, of major interest, their photocatalytic applications are hampered by several drawbacks, consisting of prompt charge recombination of charge carriers, low surface area, inactive under visible light, and inefficient as well as expensive post-treatment recovery. The immobilization of metal oxide semiconductors on materials possessing high binding strength eliminates the impractical and costly recovery of spent catalysts in large-scale operations. Notably, the synthesis of green material (ash, clay, foundry sand, and pumice)-based metal oxides could provide a synergistic effect of the superior adsorption capacity of supporting materials and the photocatalytic activity of metal oxides. This phenomenon significantly improves the overall degradation efficiency of emerging pollutants. Inspired by the novel concept of “treating waste with waste”, this contribution highlights recent advances in the utilization of natural material (clay mineral and pumice)- and waste material (ash and foundry sand)-based metal oxide nanocomposites for photodegradation of various pollutants. First, principles, mechanism, challenges towards using metal oxide as photocatalysts, and immobilization techniques are systematically summarized. Then, sources, classifications, properties, and chemical composition of green materials are briefly described. Recent advances in the utilization of green materials-based metal oxide composites for the photodegradation of various pollutants are highlighted. Finally, in the further development of green materials-derived photocatalysts, we underlined the current gaps that are worthy of deeper research in the future.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...