A stomata-inspired superhydrophobic portable filter system†
Abstract
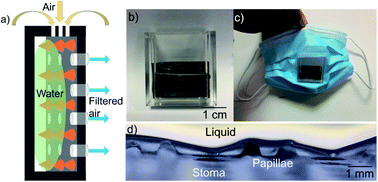
Stomata, specialized functional openings distributed on the leaf surface, are used for plant respiration by allowing gas exchange, i.e., taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, and for water content regulation. Their function is vital to plant survival. Leaves with different wettability exhibit different stomata densities. In this study, we find that stomata on Pistia stratiotes L. leaves are protected by superhydrophobic setae, which prevent direct contact between the stomata and water in humid environments by suspending water droplets on the top of the setae. Thus, oxygen and carbon dioxide are freely exchanged through the stomata. This structure inspired us to design and develop a mask for filtering solid particles and noxious gas from the atmosphere. The incoming gas is in convective contact with water, achieving a filtering efficiency. The solid particles and potential harmful gas in air are wetted and captured by water, leaving fresh air for healthy breathing. This novel design has potential applications in the treatment of respiratory diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...