Recovery, reusability and stability studies of beta cyclodextrin used for cholesterol removal from shrimp lipid
Abstract
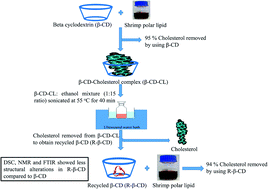
Beta cyclodextrin (β-CD) was used for cholesterol removal from shrimp lipid using ethyl acetate and water as solvents. The cholesterol incorporating β-CD complex (β-CD–CL) was collected and β-CD recovery was performed using a β-CD–CL : ethanol mixture (1 : 15 ratio) with the aid of ultrasonication and a water bath at 55 °C for 40 min. Recycled β-CD (R-β-CD) was compared with pure β-CD (P-β-CD) for the reusability of cholesterol removal from shrimp lipid. R-β-CD showed 94% cholesterol removal, while 95% was achieved for P-β-CD. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) showed a slight decrease in the melting point of R-β-CD. Nevertheless, FTIR and NMR results revealed that functional groups and the proton spectrum of R-β-CD was negligibly altered. Fatty acid contents of treated oil were slightly higher when treated with R-β-CD than those of the lipid subjected to P-β-CD treatment. Reusability of β-CD could be achieved as confirmed by the maintained capacity in cholesterol removal and unaltered structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...