Polymer films doped with fluorescent sensor for moisture and water droplet based on photo-induced electron transfer†
Abstract
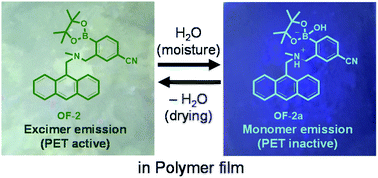
Anthracene-(aminomethyl)phenylboronic acid pinacol ester (AminoMePhenylBPin) OF-2 acts as a PET (photo-induced electron transfer)-type fluorescent sensor for determination of a trace amount of water: the addition of water to organic solvents containing OF-2 causes a drastic and linear enhancement of fluorescence emission as a function of water content, which is attributed to the suppression of PET. Indeed, detection limits (DLs) for OF-2 were as low as 0.01–0.008 wt% of water in solvents, that is, the PET method makes it possible to visualize, detect, and determine a trace amount of water. Thus, in this work, in order to develop fluorescent polymeric materials for visualization and detection of water, we have achieved the preparation of various types of polymer films (polystyrene (PS), poly(4-vinylphenol) (PVP), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and polyethylene glycol (PEG)) which were doped with OF-2, and investigated the optical sensing properties of the OF-2-doped polymer films for water. As-prepared OF-2-doped polymer films initially exhibited green excimer emission in the PET active state, but blue monomer emission in the PET inactive state upon exposure to moisture or by water droplet. Moreover, it was found that the OF-2-doped polymer films show the reversible fluorescence properties in the dry–wet process. Herein we propose that polymer films doped with PET-type fluorescent sensors for water based on a fluorescence enhancement (turn-on) system are one of the most promising and convenient functional materials for visualizing moisture and water droplets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...