Spirocyclic derivatives as antioxidants: a review†
Abstract
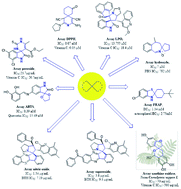
In recent years, spiro compounds have attracted significant interest in medicinal chemistry due to their numerous biological activities attributed primarily to their versatility and structural similarity to important pharmacophore centers. Currently, the development of drugs with potential antioxidant activities is of great importance since numerous investigations have shown that oxidative stress is involved in the development and progression of numerous diseases such as cancer, senile cataracts, kidney failure, diabetes, high blood pressure, cirrhosis, and neurodegenerative diseases, among others. This article provides an overview of the synthesis and various antioxidant activities found in naturally occurring and synthetic spiro compounds. Among the antioxidant activities reviewed are DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, anti-LPO, superoxide, xanthine oxidase, peroxide, hydroxyl, and nitric oxide tests, among others. Molecules that presented best results for these tests were spiro compounds G14, C12, D41, C18, C15, D5, D11, E1, and C14. In general, most active compounds are characterized for having at least one oxygen atom; an important number of them (around 35%) are phenolic compounds, and in molecules where this functional group was absent, aryl ethers and nitrogen-containing functional groups such as amine and amides could be found. Recent advances in the antioxidant activity profiles of spiro compounds have shown that they have a significant position in discovering drugs with potential antioxidant activities.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...