In silico and in vitro design of cordycepin encapsulation in liposomes for colon cancer treatment†
Abstract
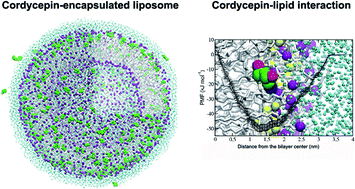
Cordycepin or 3′-deoxyadenosine is an interesting anti-cancer drug candidate that is found in abundance in the fungus Cordyceps militaris. It inhibits cellular growth of many cancers including lung carcinoma, melanoma, bladder cancer, and colon cancer by inducing apoptosis, anti-proliferation, anti-metastasis and by arresting the cell cycle. Cordycepin has, however, poor stability and low solubility in water, resulting in loss of its bioactivity. Liposomes can be used to overcome these obstacles. Our aim is to improve cordycepin's anti-colon cancer activity by liposome encapsulation. Cordycepin-encapsulated liposomes were designed and fabricated based on a combination of theoretical and experimental studies. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and free energy calculations suggest that phosphatidylcholine (PC) lipid environment is favorable for cordycepin adsorption. Cordycepin passively permeates into PC lipid bilayers without membrane damage and strongly binds to the lipids' polar groups by flipping its deoxyribose sugar toward the bilayer center. Our fabricated liposomes containing 10 : 1 molar ratio of egg yolk PC : cholesterol showed encapsulation efficiency (%EE) of 99% using microfluidic hydrodynamic focusing (MHF) methods. In our in vitro study using the HT-29 colon cancer cell line, cordycepin was able to inhibit growth by induction of apoptosis. Cell viability was significantly decreased below 50% at 125 μg mL−1 dosage after 48 h treatment with non-encapsulated and encapsulated cordycepin. Importantly, encapsulation provided (1) a 2-fold improvement in the inhibition of cancer cell growth at 125 μg mL−1 dosage and (2) 4-fold increase in release time. These in silico and in vitro studies indicate that cordycepin-encapsulated liposomes could be a potent drug candidate for colon cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...