Theoretical study of the H/D isotope effect of CH4/CD4 adsorption on a Rh(111) surface using a combined plane wave and localized basis sets method
Abstract
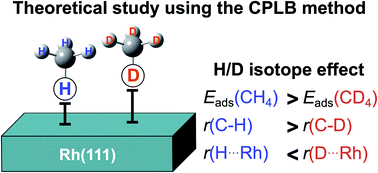
We analysed the H/D isotope effect of CH4/CD4 adsorption on a Rh(111) surface using our combined plane wave and localized basis sets method, that we proposed for the consideration of delocalized electrons on a surface and the quantum effect of protons (deuterons) in metal–molecule interactions. We observed that the adsorption distance and energy of CD4 were larger and lower than those of CH4, respectively. This is in reasonable agreement with the corresponding experimental results of cyclohexane adsorption. We clearly found that the trend of the H/D isotope effect in the geometrical and energetic difference was similar to that of the hydrogen-bonded systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...