A novel donor–π–acceptor halochromic 2,6-distyrylnaphthalene chromophore: synthesis, photophysical properties and DFT studies†
Abstract
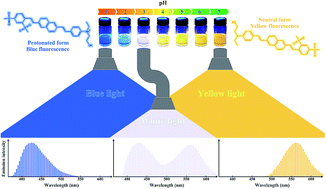
In this study a new 2,6-distyryl naphthalene [2-((4-((E)-2-(6-((E)-2,4-bis(methylsulfonyl)styryl)naphthalen-2-yl)vinyl)phenyl)(ethyl)amino)ethan-1-ol; ASDSN] was synthesized successfully using Heck chemistry as the main reaction. The ASDSN compound is a donor–pi–acceptor (D–π–A) conjugated system with amino as electron donating and sulfonyl as electron withdrawing groups. The UV-vis absorption of ASDSN was observed in the range of 403–417 nm with high molar extinction coefficients (ε = 15 300–56 200 M−1 cm−1) in some different solvents. This new fluorescent 2,6-distyryl naphthalene compound emits in the yellow region of the visible spectrum (557 nm) with Stokes shifts of 5930 cm−1. ASDSN is a pH-responsive fluorescence compound that shows yellow fluorescence in neutral form and blue fluorescence in the protonated form. A white light emission (WLE) for the chromophore was observed at pH = 3.0. The ASDSN chromophore presented a satisfactory white light quantum yield (Φ) of 13% which was desirable for producing white light emitting devices. Density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent (TD)-DFT were applied to study structural and electronic properties of the chromophore.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...