Tuning of structural and optical properties with enhanced catalytic activity in chemically synthesized Co-doped MoS2 nanosheets†
Abstract
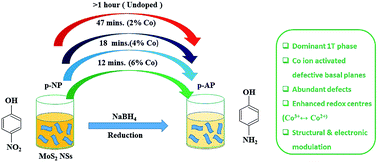
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets, due to having a highly active nature, being low cost and having unique physical and chemical properties, have shown their efficacy in the catalytic reduction of nitroarenes. Doping of transition metal ions in molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets is a well-known strategy to enhance their catalytic efficiency for the reduction of nitroarenes, however, finding the optimum dopant amount is still a subject of ongoing research. Herein, we have synthesized few-layered cobalt (Co) doped MoS2 nanosheets with different cobalt content (2%, 4%, 6% and 8%) through the solvothermal approach, taking sodium molybdate dihydrate (Na2MoO4·2H2O), thiourea (CH4N2S) and cobalt acetate tetrahydrate [Co(CH3COO)2·4H2O] as precursors and their catalytic performance has been affirmed by monitoring the reduction of p-nitrophenol by NaBH4 in real time using UV-visible absorption spectroscopy. The 6% Co doped MoS2 nanosheets have exhibited superior catalytic activity with a pseudo-first order rate constant of 3.03 × 10−3 s−1 attributed to the abundant defects in the active edge sites having a dominant metallic 1T phase with Co ion activated defective basal planes, sulphur (S) edges, synergistic structural and electronic modulation between MoS2 and Co ions and enhanced electron transfer assisted through redox cycling in the active sites. An attempt has also been made to study the manipulation of structural and optical properties with cobalt doping in MoS2 nanosheets to establish a correlation between the catalytic efficiency and dopant content. This study demonstrates that proper tuning of Co doping in MoS2 nanosheets paves the way in searching for a potential alternative of a noble metal catalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitroarenes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...