Phenolate anion-catalyzed direct activation of inert alkyl chlorides driven by visible light†
Abstract
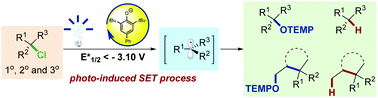
Alkyl chlorides are abundant and stable chemical feedstocks, but their chemical inertness hinders their widespread availability as reactants in synthetic chemistry. In this study, we demonstrate an efficient photochemical strategy to activate inert C(sp3)–Cl bonds catalyzed by phenolate anion photocatalysts. Mechanistic studies indicate that the cleavage of unactivated C(sp3)–Cl bonds is mediated by a direct SET process from photo-excited phenolate anions. This strategy conveniently engages a diverse range of unactivated primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl chlorides in radical C–O bond formation, dehalogenation, and cyclization under mild conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...