Modification of polybutadiene with trifluoromethyl and clickable azide groups in one shot†
Abstract
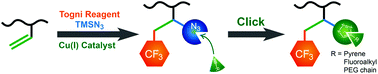
Development of facile synthetic routes to endow polybutadiene (PB) with desirable and/or enhanced properties has attracted growing attention owing to the broad application spectrum of PB. Herein, we report an efficient approach to introduce both trifluoromethyl (–CF3) and azide (–N3) groups into PB in a one-shot procedure via copper-catalyzed azide-trifluoromethylation of the alkenyls of PB using Cu(CH3CN)4PF6 as the catalyst and commercially available Togni's reagent and TMSN3 as –CF3 and –N3 sources, respectively, without chain cross-linking or chain degradation. The contents of –CF3 and –N3 in PB increase with the increasing feed ratio of –CF3 and –N3 sources to the alkenyl of PB. After the modification, the glass transition temperatures (Tg) of the resulting PBs increase from about −31.4 °C to 35.7 °C accompanied by a decrease of the thermal stability from ∼343.8 °C to ∼249.6 °C (5% weight loss temperature). The films of the resulting modified PBs exhibit more hydrophobic surfaces than pristine PB and the water contact angles increase with increasing –CF3 content. By taking advantage of the introduced azide groups as reactive anchoring sites, additional functionalities, including fluorescent pyrenes, perfluoroalkyls and short PEG chains, can be efficiently attached onto PB chains via copper-catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloaddition (CuAAC). In this way, the properties, such as thermal stability, photophysical properties and wetting behavior, of PB can be easily tuned.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...