Thiol–ene enabled preparation of S-lipidated anti-HBV peptides†
Abstract
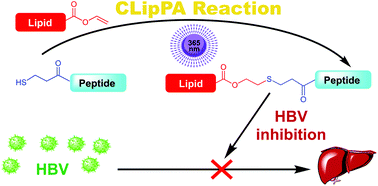
Despite significant efforts made towards treatments for Hepatitis B virus (HBV), a long-term curative treatment has thus far eluded scientists. Recently, the Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide (NTCP) receptor has been identified as the entry pathway of HBV into hepatocytes. Myrcludex B, an N-terminally myristoylated 47-mer peptide mimic of the preS1 domain of the Hepatitis B virion, was identified as a potent protein–protein interaction (PPI) inhibitor blocking HBV fusion (IC50 = 140 pM). Herein we report an optimised chemical synthesis of Myrcludex B and a series of novel analogues. Employing a small modification to the Cysteine Lipidation of a Peptide or Amino acid (CLipPA) thiol–ene reaction, a library of S-lipidated Myrcludex B and truncated (21-mer) analogues were prepared, providing novel chemical space to probe for the discovery of novel anti-HBV peptides. The S-lipidated analogues showed an equivalent or a slight decrease (∼2-fold) in binding effectiveness to NTCP expressing hepatocytes compared to Myrcludex B. Three S-lipidated analogues were highly potent HBV inhibitors (IC50 0.97–3.32 nM). These results demonstrate that incorporation of heteroatoms into the lipid ‘anchor’ is tolerated by this antiviral scaffold and to the best of our knowledge constitutes the first report of potent S-lipidated antiviral peptides. Interestingly, despite only moderate reductions in binding effectiveness, truncated analogues possessed dramatically reduced inhibitory activity thus providing new insights into the structure activity relationship of these hitherto unreported antiviral S-lipopeptides.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...