A nanoparticle-containing polycaprolactone implant for combating post-resection breast cancer recurrence
Abstract
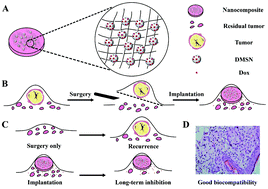
The recurrence and metastasis of tumor after surgery is the main cause of death for patients with breast cancer. Systemic chemotherapy suffered from low delivery efficiency to tumors and the side effects of chemo drugs. Localized chemotherapy using drug-containing implants is an alternative, while the reconstruction of breast tissue is generally considered after chemotherapy, resulting in a second surgery for patients. Here, we describe a strategy using implantable drug-containing polymeric scaffolds to deliver chemo drugs directly to the post-resection site, and simultaneously provide mechanical support and regenerative niche for breast tissue reconstruction. When doxorubicin was loaded in mesoporous silica nanoparticles and subsequently incorporated into polycaprolactone scaffolds (DMSN@PCL), a 9-week sustained drug release was achieved post implantation in mice. The local recurrence of residual tumor after surgery was significantly inhibited within 4 weeks in a post-surgical mouse model bearing xenograft MDA-MB-231 tumor. DMSN@PCL scaffolds exhibited good biocompatibility in mice during the treatment. We believe our strategy holds great promise as an adjuvant localized chemotherapy in clinics for combating post-resection breast cancer recurrence.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Advanced Functional Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...