Partial sulfur vacancies created by carbon–nitrogen deposition of MoS2 for high-performance overall electrocatalytic water splitting†
Abstract
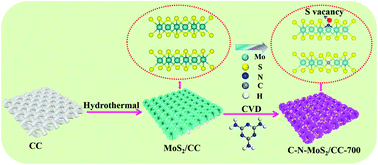
Electrocatalytic water splitting is a promising energy-efficient solution to obtain clean hydrogen energy. Bifunctional electrocatalysts made up of cheap and abundant elements and suitable for both the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) are critically needed, yet their performance deserves substantial improvement. The catalytic activity could be improved by creating unsaturated defects, which so far has rarely been demonstrated. Here, we combine the effects of unsaturated sulfur vacancies and bi-elemental C and N doping in MoS2 nanosheets to achieve high-performance bifunctional electrocatalysts. The new method to obtain C and N doped MoS2 at high temperature is presented. The obtained C–N-MoS2/CC-T catalysts with S unsaturated defect sites and Mo–N links exhibit high activity and improved electrical conductivity for both the HER and OER in alkaline media. Systematic experiments and density functional theory (DFT) analysis confirm that CN-doping exposes catalytically active sites and enhances water adsorption. The optimized C–N-MoS2/CC-700 catalyst exhibits low overpotentials of 90 and 230 mV at 10 mA cm−2 for the HER and OER, respectively. Importantly, the porous C–N-MoS2/CC-700 nanosheets deliver low voltages of 1.58 V for the overall water splitting at 10 mA cm−2 and robust operation for 30 h without any reduced activity. Such impressive performances are attributed to their unique structure with large specific surface area, abundant S unsaturated sites, Mo–N links, and shortened electron transfer paths. This partial defect filling by the bi-dopant incorporation approach is generic and is promising for a broad range of advanced energy materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...