The selective deprotonation of carbon quantum dots for fluorescence detection of phosphate and visualization of latent fingerprints†
Abstract
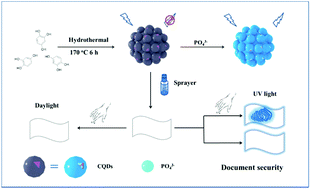
We developed a water-soluble, stable and selective “turn-on” fluorescence sensing platform based on carbon quantum dots (CQDs) for rapid determination of phosphate (Pi) in aqueous solutions and for visualization of latent fingerprints on paper. The hydroxyl groups on the surface of the synthesized CQDs can be deprotonated by Pi to trigger the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) process and the inhibition of excited-state proton transfer (ESPT), achieving a turn-on emission response. CQDs demonstrated the capability to selectively detect Pi over other common ions and biomolecules with the linear fluorescence intensity change in the range from 0 to 100 μM. Moreover, the paper sprayed with the CQD solution showed a remarkable blue emission speckle and a fingerprint upon addition of Pi solution and finger touching, respectively. Notably, the fingerprint images including level 3 details (crossover, bifurcation, termination, and island and sweat pores) are also clearly identified and distinguished, indicating their potential application in document security. We believe that the as-synthesized CQDs will provide a new tool for Pi detection in aqueous media and paper document security.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...