Abstract
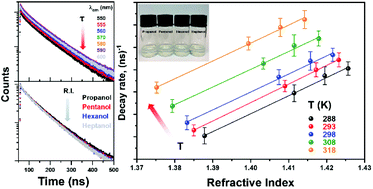
The spontaneous emission rate (SER) of a chromophore in a nanoparticle (NP) is determined by the modification of the electric field by its environment. Previous studies of this local field effect have dispersed NPs in non-chemically interacting media of different refractive index (RI) and measured the emission lifetimes. Unfortunately, the applicable solvents cover only a small range of RI so that the test of a theoretical model is limited. We have utilized the variation of temperature to modify RI so that a more comprehensive test of a model can be achieved. Yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG) NPs doped with Ce3+ ions were immersed in different alcohols and the lifetime of the electric dipole allowed 5d1 → 4f1 transition was measured at different temperatures in each case. In order to clarify and confirm our results we have employed two different dopant concentrations of Ce/Y, near 1.3 at% and 0.13 at%. The Ce3+ lifetimes were well-fitted to a formula relating the decay rate to the dielectric parameters of the nanocomposite and the volumetric content of the NPs. Two parameters were derived: the SER of the bulk material (found to be effectively constant) and the nonradiative decay rate, which varied as the multiphonon relaxation rate for the more heavily-doped materials. The emission from the YAG:Ce3+ NPs was attributed to Ce3+ ions with 8-coordination to oxygen in addition to surface Ce3+ ions with lower coordination number. The bulk radiative lifetime was determined as 66 ± 3 ns.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...