Prediction of chemically ordered dual transition metal carbides (MXenes) as high-capacity anode materials for Na-ion batteries†
Abstract
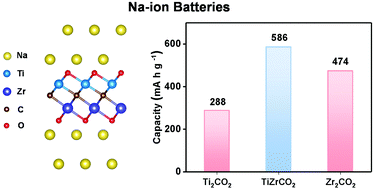
Na-ion batteries have attracted tremendous attention. In this work, various electrochemical properties of three titanium zirconium dual transition metal carbides (TiZrCO2, Ti2ZrC2O2, and TiZr2C2O2) as anode materials for Na-ion batteries are systemically investigated by using density functional theory calculations. Firstly, all these three systems are dynamically stable and exhibit good conductivities. Besides, all of them can realize energetically favorable double-layer adsorption of Na atoms on each side, which endows them with obviously higher capacities than their corresponding mono-titanium- and zirconium-based MXenes. Moreover, their low diffusion energy barriers (<0.3 eV) and suitable open circuit voltages further indicate that these three titanium zirconium dual transition metal carbides are promising anode materials for Na-ion batteries. More importantly, our work opens an avenue to exploit other dual transition metal carbides as high-performance anode materials for Na-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...