Recent progress in electrochemical performance of binder-free anodes for potassium-ion batteries
Abstract
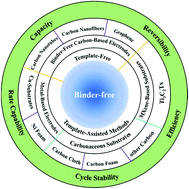
Potassium ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising candidates for large-scale stationary energy storage beyond lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), owing to the abundance of potassium resources and low cost. Unfortunately, the practical application of PIBs is severely restricted by their poor rate capacity and unsatisfactory cycle performance. In traditional electrodes, a binder usually plays an important role in integrating individual active materials with conductive additives. Nevertheless, binders are not only generally electrochemically inactive but also insulating, which is unfavorable for improving overall energy density and cycling stability. To this end, in terms of both improved electronic conductivity and electrochemical reaction reversibility, binder-free electrodes offer great potential for high-performance PIBs. Moreover, the anode is a crucial configuration to determine full cell electrochemical performance. Therefore, this review analyzes in detail the electrochemical properties of the different type binder-free anodes, including carbon-based substrates (graphene, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, and so on), MXene-based substrates and metal-based substrates (Cu and Ni). More importantly, the recent progress, critical issues, challenges, and perspectives in binder-free electrodes for PIBs are further discussed. This review will provide theoretical guidance for the synthesis of high-performance anode materials and promote the further development of PIBs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...