A hydrogel-based implantable multidrug antitubercular formulation outperforms oral delivery†
Abstract
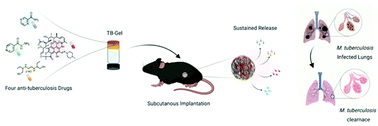
We present a non-immunogenic, injectable, low molecular weight, amphiphilic hydrogel-based drug delivery system (TB-Gel) that can entrap a cocktail of four front-line antitubercular drugs, isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. We showed that TB-Gel is more effective than oral delivery of the combination of four drugs in reducing the mycobacterial infection in mice. Results show that half the dose of chemotherapeutic drugs is sufficient to achieve a comparable therapeutic effect to that of oral delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...