An intelligent T1–T2 switchable MRI contrast agent for the non-invasive identification of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques†
Abstract
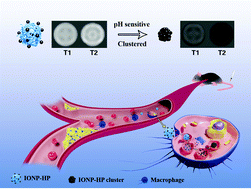
Unlike stable atherosclerotic plaques, vulnerable plaques are very likely to cause serious cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Meanwhile, how to non-invasively identify vulnerable plaques at early stages has been an urgent but challenging problem in clinical practices. Here, we propose a macrophage-targeted and in situ stimuli-triggered T1–T2 switchable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) nanoprobe for the non-invasive diagnosis of vulnerable plaques. Precisely, single-dispersed iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) modified with hyaluronic acid (HA), denoted as IONP-HP, show macrophage targetability and T1 MRI enhancement (r2/r1 = 3.415). Triggered by the low pH environment of macrophage lysosomes, the single-dispersed IONP-HP transforms into a cluster analogue, which exhibits T2 MRI enhancement (r2/r1 = 13.326). Furthermore, an in vivo switch of T1–T2 enhancement modes shows that the vulnerable plaques exhibit strong T1 enhancement after intravenous administration of the nanoprobe, followed by a switch to T2 enhancement after 9 h. In contrast, stable plaques show only slight T1 enhancement but without T2 enhancement. It is therefore imperative that the intelligent and novel nanoplatform proposed in this study achieves a substantial non-invasive diagnosis of vulnerable plaques by means of a facile but effective T1–T2 switchable process, which will significantly contribute to the application of materials science in solving clinical problems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...