General and mild modification of food-derived extracellular vesicles for enhanced cell targeting†
Abstract
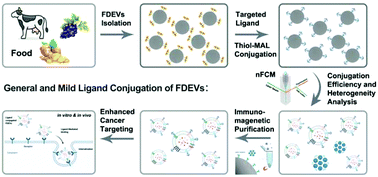
Food-derived extracellular vesicles (FDEVs) have attracted increasing attention as potential delivery vehicles for therapeutic agents due to their desirable features such as excellent biocompatibility, easy accessibility and cost effectiveness. However, the intrinsic targeting capability of FDEVs is unsatisfactory compared to artificial nanoparticles or other source-derived EVs, which calls for efficient surface engineering strategies to equip them with specific ligands. Here we report a general and mild modification method via reduction of disulfide groups to maleimide reactive thiols. Taking milk-derived EVs (mEVs) as a model system, we demonstrated the feasibility for tethering various ligands on the surface without compromising the vesicular structures. Building an ultra-sensitive nano-flow cytometer (nFCM), the heterogeneous nature of the functionalized samples was revealed, and a magnetic separation approach was proposed accordingly to remove the as-observed non-EV particles. The cellular uptake and cytotoxicity experiments provided direct evidence showing an enhanced cell targeting and cargo delivery capability of the ligand conjugated mEVs. In addition, the in vivo imaging further proved the applicability of transferrin conjugation for increased tumor enrichment of mEVs. Collectively, this general and mild ligand conjugation method enables an efficient surface functionalization of FDEVs, which is of vital importance for enhanced targeting delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...