The recovery of nano-sized carbon black filler structure and its contribution to stress recovery in rubber nanocomposites†
Abstract
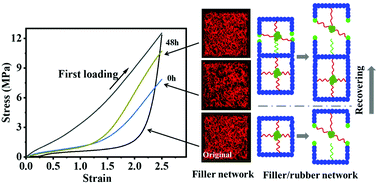
The hierarchical structural evolution of natural rubber (NR) filled with different contents of nanoscale carbon black (CB) (10 phr-CB10 and 50 phr-CB50) after first loading and recovering for different times was investigated by X-ray nano-CT, wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) and solid state NMR techniques. The CB filler structures as captured by X-ray nano-CT recover gradually with increasing recovering time, but the filler network with different CB contents shows dramatically different structure evolution. For CB10, limited by the filling content, CB particles mainly induces a hydrodynamic effect in spite of deformation or recovering. For CB50, the CB filler forms a 3D connected network, partially destructed during deformation, and the destructed part can be partially recovered during recovery. This suggests that the connected CB filler structure mainly acts as a network reinforcement, whereas the destructed part can induce a hydrodynamic effect. The different effects induced by different CB filling contents are also reflected by the NR matrix, which is reflected by the onset strains εc of strain-induced crystallization (SIC) of NR as captured by WAXS. For CB10, εc remains almost constant, i.e. εc = ca. 1.49, while that of NR with CB50 slightly decreases from initial ca. 1.12 to 0.96 with increasing recovering time up to 50 h. Also, the bound rubber fraction and entangled rubber network remain unchanged after deformation and under different recovery time as detected by the magic sandwich echo (MSE) FID and proton multiple quantum (MQ) NMR. These results demonstrate the key role of the CB filler network in determining the stress-softening behavior of reinforced rubber.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...