Metabolic engineering for plant natural products biosynthesis: new procedures, concrete achievements and remaining limits
Abstract
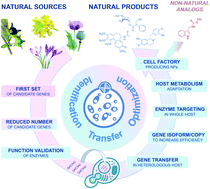
Microorganisms and plants represent major sources of natural compounds with a plethora of bioactive properties. Among these, plant natural products (PNPs) remain indispensable to human health. With few exceptions, PNP-based pharmaceuticals come from plant specialized metabolisms and display a structure far too complex for a profitable production by total chemical synthesis. Accordingly, their industrial processes of supply are still mostly based on the extraction of final products or precursors directly from plant materials. This implies that particular contexts (e.g. pandemics, climate changes) and natural resource overexploitation are main drivers for the high production cost and recurrent supply shortages. Recently, biotechnological manufacturing alternatives gave rise to a multitude of benchmark studies implementing the production of important PNPs in various heterologous hosts. Here, we spotlight unprecedented advancements in the field of metabolic engineering dedicated to the heterologous production of a prominent series of PNPs that were achieved during the year 2020. We also discuss how the knowledge accumulated in recent years could pave the way for a broader manufacturing palette of natural products from a wide range of natural resources.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...