The role of mono- and dicarboxylic acids in the building of oxomolybdates containing {MoO4}, {Mo2O5}, {Mo2O6}, {Mo3O8}, {Mo5O17}, {Mo5O18}, {Mo8O26}, and {SiMo12O40} units†
Abstract
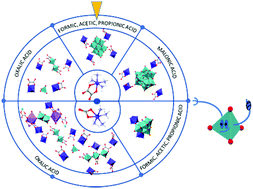
Seven tetraammineoxalatocobalt(III) salts with oxomolybdate anions of different nuclearities, such as [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]2[MoO4]·H2O (1), [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]2[Mo2O4(μ-O)(C2O4)2(H2O)2]·4H2O (3), Na2[Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]2[Mo2O4(μ-O)2(C2O4)2]·4H2O (4), [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]4[Mo3O6(μ-O)2(C2O4)3(H2O)2]·5H2O (5), [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]4[Mo8O26]·12H2O (8), [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]4[SiMo12O40]·6H2O (9) and [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]4[Mo8O26]·10H2O (10), along with [Mo5Co2O17(HCO3)(H2C3O4H)(NH3)7]·5H2O (6) and [Mo5Co2O18(NH3)7]·5H2O (7), were isolated using a one-pot reaction of sodium molybdate with [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]NO3·H2O or [Co(CO3)(NH3)4]NO3· H2O and mono- or dicarboxylic acids in an aqueous medium. Polyoxomolybdate anions are built up from {MoO4}, {Mo2O4(μ-O)}, {Mo2O4(μ-O)2}, {Mo3O6(μ-O)2}, {Mo5O17}, {Mo5O18}, {Mo8O26} and {SiMo12O40} units, respectively, depending on the nature of the carboxylic acid additive used in the synthesis. The isolation of these salts confirmed that the carboxylic acids act not only as ligands, primarly, but also as structure-directing agents in the polyoxoanion self-assembly processes. All products were characterized in the solid state via single-crystal and powder X-ray diffraction, infrared spectroscopy as well as thermogravimetric and elemental analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...