Synthesis of model bacteriochlorophylls containing substituents of native rings A, C and E†
Abstract
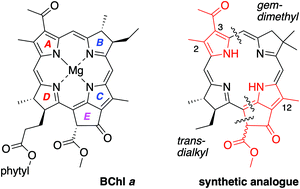
A route under development for the synthesis of bacteriochlorophyll a and analogues relies on joining an AD-dihydrodipyrrin (bearing a D-ring carboxaldehyde) and a BC-dihydrodipyrrin (bearing a C-ring β-ketoester group and a B-ring dimethoxymethyl group) via Knoevenagel condensation followed by double-ring closure (Nazarov cyclization, electrophilic aromatic substitution, and elimination of methanol). Prior synthetic studies afforded the bacteriochlorophyll skeleton containing a gem-dimethyl group in ring B, a trans-dialkyl group in ring D, and a carboethoxy group at the 3-position of ring A. To explore the incorporation of native substituents, the synthesis of two bacteriochlorophyll analogues thereof was pursued, one with 12-methyl and 3-carboethoxy groups and the other with 2,12-dimethyl and 3-acetyl groups. The 12-methyl group resulted in half the yield (versus the unsubstituted analogue) in the Knoevenagel reaction, but insignificant effects in all other steps including the rate and yield of double-ring closure despite the known effects of alkyl groups to facilitate electrophilic substitution of pyrroles. The 2-methyl-3-acetyl group, however, resulted in diminished yields in several steps, including the Knoevenagel reaction, but not the double-ring closure. The results point to obstacles and openings on the path to total syntheses of the native pigments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...