Polymyxin B-functionalized phthalocyanine for chemo-photodynamic antibacterial therapy in enhanced wound healing†
Abstract
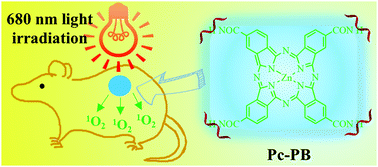
This paper proposes synergistic photodynamic antimicrobial therapy and chemotherapy for enhanced wound healing using polymyxin B-functionalized phthalocyanine (Pc-PB) as a new photosensitive antibacterial agent. The rapid healing of a bacteria-infected wound was achieved via combining the photodynamic antibacterial activity of phthalocyanine with the innate antibacterial ability of polymyxin B. After the functionalization of polymyxin B, the new phthalocyanine derivative can effectively target the bacterial surface and generate singlet oxygen to kill Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria under 680 nm light irradiation. Additionally, the prepared Pc-PB can form colloidal nanoparticles to significantly increase the solubility and dispersion of phthalocyanine in water. For the antimicrobial action mechanism, the antibacterial agent can interact with bacteria via binding to the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions of the bacterial surface and then disrupting the bacterial membrane. Pc-PB shows good biocompatibility and can promote the healing of bacteria-infected wounds. These results suggest that phthalocyanine combined with bioactive molecules has potential for application in photodynamic therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...