Significant role of thorny surface morphology of polyaniline on adsorption of triiodide ions towards counter electrode in dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
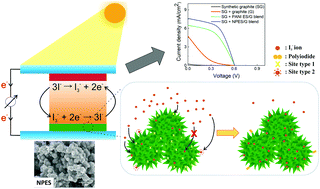
This paper investigates the adsorption behavior of polyaniline (PANI) towards triiodide ion (I3−) solution in acetonitrile. Two different types of PANI, namely PANI emeraldine salt (PANI ES) and nanostructured PANI ES (NPES) were prepared by the rapid mixing and interfacial polymerization methods, respectively. FTIR and Raman spectroscopy results show that both PANI ES and NPES have similar vibrational features, indicating a similar molecular structure. NPES particles are interconnected granules with thorny durian-like surface morphology and better shape uniformity than PANI ES. The maximum adsorption capacity of NPES towards triiodide (I3−) ions is higher than that of PANI ES; however, both of them obey the dual-site Langmuir–Freundlich isotherm. The calculated thermodynamic parameters reveal the spontaneous and endothermic adsorption processes for both types of PANI. The positively charged group in PANI (C–N+) provides more favorable adsorption sites for I3− ions through electrostatic interactions, as confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. The photovoltaic and electrochemical performance data confirm the higher power conversion efficiency (∼30%) of the NPES counter electrode compared to that of PANI ES. The thorny durian-like surface morphology of NPES enhances the number of adsorption sites for I3− ions, thereby facilitating better electrolyte regeneration in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...