Metal–organic framework derived metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite, a new tool for the determination of dipyridamole†
Abstract
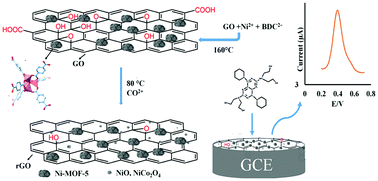
Dipyridamole is a prescribed medication used to treat cardiovascular diseases, angina pectoris, and myocardial infarction, and in imaging tests for heart patients. Therefore, a high selectivity and sensitivity, low cost, and high-performance speed test is needed to monitor this compound. In this work, a sensitive, selective, and rapid electrochemical sensor is developed based on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) modified with MOF derived-NiCo2O4/NiO/rGO to determine dipyridamole by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The NiCo2O4/NiO@MOF-5/rGO was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, map analysis, and FT-IR spectroscopic methods. The electrochemical behavior of dipyridamole at the surface of the modified electrode was investigated. After the optimization of the experimental parameters, it was shown that the designed sensor could determine dipyridamole with a limit of detection of 2.8 nM and a linear range of 0.02–550 μM. Ultimately, the proposed sensor could determine the dipyridamole concentration in biological samples with high accuracy using certified validation in recoveries ranging from 97.7% to 104.6%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...