Nickel(ii) di-aqua complex containing a water cluster: synthesis, X-ray structure and catecholase activity†
Abstract
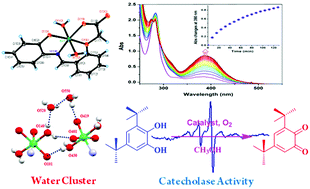
A trans-diaquanickel(II) complex of the type [(L2−)NiII(H2O)2]·nH2O (1·nH2O) was isolated, where LH2 is (E)-2-(2-((2-hydroxyphenylimino)methyl)phenoxy)acetic acid (LH2), a tetradentate ligand. The molecular geometry of 1·nH2O was confirmed by single crystal X-ray structure determination. It is observed that in the crystal, coordinated water, bulk water and ligand oxygen atoms form six membered water clusters by OH⋯H interactions. 1·nH2O has emerged as a catalyst for the oxidation of 3,5-di-tert-butylcatecholto 3,5-di-tert-butyl-o-benzoquinone with a turnover number (kcat) of 4.46 × 102 h−1 in CH3OH. During oxidation, the coordination of catechol to the nickel(II) centre and the formation of an o-benzosemiquinone intermediate were confirmed by a nickel based EPR signal, ESI mass spectrometry and UV-vis spectra. 1·nH2O exhibits an irreversible anodic peak at 0.83 V versus the Fc+/Fc couple due to the phenoxyl/phenolato redox couple, authenticated by DFT calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...