Tumor-targeted gene therapy with lipid nanoparticles inhibits tumor-associated adipocytes and remodels the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in triple-negative breast cancer†
Abstract
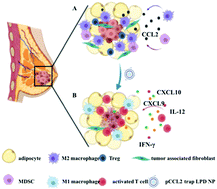
Adipocytes are the primary cellular components within the tumor microenvironment (TME) of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Increasing evidence suggests that tumor-associated adipocytes (TAAs) can aggravate tumor progression, exacerbate the immunosuppressive TME and compromise therapeutic efficacy. In this study, the biological effect of TAAs within the breast cancer TME is first investigated, and the C–C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 (CCL2) which is mainly secreted by TAAs in the extracellular environment is identified as the key mediator. CCL2 recruits immune cells such as monocytes and macrophages that further differentiated into immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and M2 macrophages. To manipulate CCL2-mediated immune response, a protein trap that binds with CCL2 with high affinity and specificity is designed. The plasmid DNA encoding the CCL2 trap (pCCL2) is specifically delivered to the TME by using targeted lipid-protamine-DNA (LPD) nanoparticles to locally express the CCL2 trap and ameliorate the immunosuppressive TME. Significantly, compared with the commercially available CCL2 antibody, this strategy shows enhanced therapeutic efficacy and appreciable tumor growth inhibition. Furthermore, the pCCL2 trap treatment successfully suppresses TAAs, increases T cell infiltration and decreases the population of immunosuppressive M2 macrophages and MDSCs. Further studies show that the pCCL2 trap could facilitate PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy, demonstrating its translation potential.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Nanoscale and Nanoscale Horizons: Nanobiotechnology and Nanomedicine and Nanoscale Horizons Most Popular 2021 Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...