Pentacene/perfluoropentacene bilayers on Au(111) and Cu(111): impact of organic–metal coupling strength on molecular structure formation†
Abstract
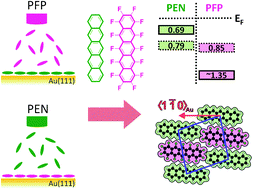
As crucial element in organic opto-electronic devices, heterostructures are of pivotal importance. In this context, a comprehensive study of the properties on a simplified model system of a donor–acceptor (D–A) bilayer structure is presented, using ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) and normal-incidence X-ray standing wave (NIXSW) measurements. Pentacene (PEN) as donor and perfluoropentacene (PFP) as acceptor material are chosen to produce bilayer structures on Au(111) and Cu(111) by sequential monolayer deposition of the two materials. By comparing the adsorption behavior of PEN/PFP bilayers on such weakly and strongly interacting substrates, it is found that: (i) the adsorption distance of the first layer (PEN or PFP) indicates physisorption on Au(111), (ii) the characteristics of the bilayer structure on Au(111) are (almost) independent of the deposition sequence, and hence, (iii) in both cases a mixed bilayer is formed on the Au substrate. This is in striking contrast to PFP/PEN bilayers on Cu(111), where strong chemisorption pins PEN molecules to the metal surface and no intermixing is induced by subsequent PFP deposition. The results illustrate the strong tendency of PEN and PFP molecules to mix, which has important implications for the fabrication of PEN/PFP heterojunctions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...