Rhodium nanoparticles inside well-defined unimolecular amphiphilic polymeric nanoreactors: synthesis and biphasic hydrogenation catalysis†
Abstract
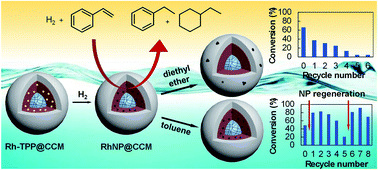
Rhodium nanoparticles (Rh NPs) embedded in different amphiphilic core-crosslinked micelle (CCM) latexes (RhNP@CCM) have been synthesized by [RhCl(COD)(TPP@CCM)] reduction with H2 (TPP@CCM = core-anchored triphenylphosphine). The reduction rate depends on temperature, on the presence of base (NEt3) and on the P/Rh ratio. For CCMs with outer shells made of neutral P(MAA-co-PEOMA) copolymer chains (RhNP@CCM-N), the core-generated Rh NPs tend to migrate toward the hydrophilic shell and to agglomerate depending on the P/Rh ratio and core TPP density, whereas the MAA protonation state has a negligible effect. Conversely, CCMs with outer shells made of polycationic P(4VPMe+I−) chains (RhNP@CCM-C) maintain core-confined and well dispersed Rh NPs. All RhNP@CCMs were used as catalytic nanoreactors under aqueous biphasic conditions for acetophenone, styrene and 1-octene hydrogenation. Styrene was efficiently hydrogenated by all systems with high selectivity for vinyl reduction. For acetophenone, competition between benzene ring and carbonyl reduction was observed as well as a limited access to the catalytic sites when using CCM-C. Neat 1-octene was also converted, but the activity increased when the substrate was diluted in 1-nonanol, which is a better core-swelling solvent. Whereas the molecular RhI center was more active than the Rh0 NPs in 1-octene hydrogenation, the opposite trend was observed for styrene hydrogenation. Although Rh NP migration and agglomeration occurred for RhNP@CCM-N, even at high P/Rh, the NPs remained core-confined for RhNP@CCM-C, but only when toluene rather than diethyl ether was used for product extraction before recycling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...