Tuning the band gap of M-doped titanate nanotubes (M = Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu): an experimental and theoretical study†
Abstract
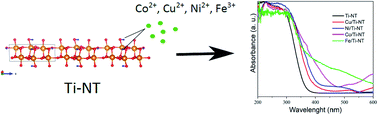
Herein, we report a systematic experimental and theoretical study about a wide-ranged band gap tuning of protonated titanate nanotubes H2Ti3O7 (Ti-NT) by an easy ion-exchange method using a low concentration (1 wt%) of transition metal cations. To characterize and describe the effect of M doping (M = Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+, and Fe3+) on the electronic, optical and structural properties, semiconductors were analyzed by a combination of experimental methods and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The nanotube band gap can be modified from 1.5 to 3.3 eV, which opens the possibility to use them in several optoelectronic applications such as photocatalysts under solar light irradiation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Latin American Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...