Abstract
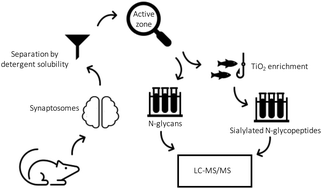
N-linked glycosylation is a ubiquitous protein modification that is capable of modulating protein structure, function and interactions. Many proteins in the brain associated with the synapse and important for synaptic transmission are highly glycosylated and their glycosylation could be important for learning and memory related molecular processes and synaptic plasticity. In the present study, we extend the knowledge of the synaptic glycome and glycoproteome by performing glycan- and intact glycopeptide-focused analyses of isolated rat nerve terminals (synaptosomes) by LC-MS/MS. Overall, glycomics identified a total of 41 N-glycans in isolated synaptosomes. Sialylated N-glycans represented only 7% of the total abundance of the rat synaptosome N-glycome with oligomannose, neutral hybrid and complex type N-glycans being the most abundant structures. Using detergent extraction of the active zone proteins from the synaptosomes revealed a change in the active zone glycan abundance in comparison with the rest of the synaptosome glycan content. Characterization of intact sialylated N-linked glycopeptides enriched by titanium dioxide chromatography revealed more than 85% selectivity of sialylated species and the presence of NeuGc on active zone proteins. In addition, both disialic and trisialic acid modified glycans were present on synaptic glycoproteins, although oxonium ion profiling revealed that trisialic units were only present on glycoproteins in the detergent soluble fraction. However, correct identification of intact sialylated N-linked glycopeptides using the Byonic program failed, most likely due to the lack of peptide backbone fragmentation during tandem mass spectrometry.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Glycomics & Glycoproteomics: From Analytics to Function


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...