Identification of stem cells from large cell populations with topological scoring†
Abstract
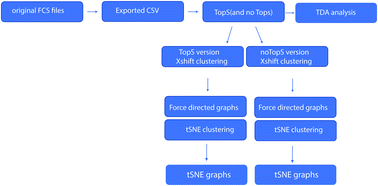
Machine learning and topological analysis methods are becoming increasingly used on various large-scale omics datasets. Modern high dimensional flow cytometry data sets share many features with other omics datasets like genomics and proteomics. For example, genomics or proteomics datasets can be sparse and have high dimensionality, and flow cytometry datasets can also share these features. This makes flow cytometry data potentially a suitable candidate for employing machine learning and topological scoring strategies, for example, to gain novel insights into patterns within the data. We have previously developed a Topological Score (TopS) and implemented it for the analysis of quantitative protein interaction network datasets. Here we show that TopS approach for large scale data analysis is applicable to the analysis of a previously described flow cytometry sorted human hematopoietic stem cell dataset. We demonstrate that TopS is capable of effectively sorting this dataset into cell populations and identify rare cell populations. We demonstrate the utility of TopS when coupled with multiple approaches including topological data analysis, X-shift clustering, and t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE). Our results suggest that TopS could be effectively used to analyze large scale flow cytometry datasets to find rare cell populations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Computational Approaches in Multi-Omics Analysis


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...