Tuneable polarity and enhanced piezoelectric response of ZnO thin films grown by metal–organic chemical vapour deposition through the flow rate adjustment†
Abstract
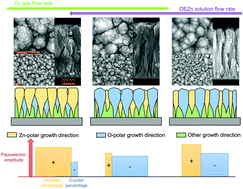
The formation process of ZnO thin films grown by pulsed-liquid injection metal–organic chemical vapour deposition (PLI-MOCVD) has a major impact on its morphological, structural, electrical and piezoelectric properties, but their correlation has not been elucidated yet nor decoupled from the thickness effects. In this work, we investigate the influence of the O2 gas and diethylzinc (DEZn) solution flow rates on the properties of ZnO thin films with a given thickness and grown on silicon. We show that the O2/DEZn flow rate ratio through the oxygen chemical potential significantly affects the O- and Zn-polarity domain distribution, their related size and shape, the chemical composition, and the incorporation of microstructural defects and residual impurities, resulting in a direct effect on the piezoelectric amplitude of ZnO thin films. In particular, the Zn-polarity domains are found to systematically exhibit a larger piezoelectric amplitude than the O-polarity domains, regardless of the O2/DEZn flow rate ratio. A comprehensive description recapitulating the formation process of ZnO thin films through three different regimes depending on the O2/DEZn flow rate ratio is further gained. These results demonstrate the crucial ability of the PLI-MOCVD system to tune the polarity of ZnO thin films along with other suitable properties for piezoelectric applications by carefully adjusting the O2 gas and DEZn solution flow rates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...