Human neuromuscular junction on micro-structured microfluidic devices implemented with a custom micro electrode array (MEA)†
Abstract
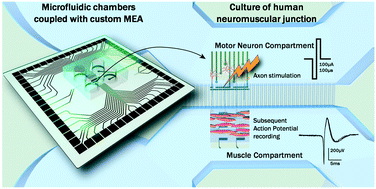
In the neuromuscular system, signal transmission from motor neurons (MNs) to innervated muscle fibers is crucial for their synaptic function, viability, and maintenance. In order to better understand human neuromuscular junction (hNMJ) functionality, it is important to develop on-a-chip devices with human cells. To investigate this cell network, microfluidic platforms are useful to grow different cell types in isolated compartments. Such devices have already been developed to study in vitro neuronal circuitry. Here, we combined microfluidics with two techniques: soft lithography and custom microelectrodes array (MEA). Our goal was to create hNMJs on a specific pattern of electrodes to stimulate pre-synaptic axons and record post-synaptic muscle activity. Micromachining was used to create structurations to guide muscle growth above electrodes, without impairing axon propagation, therefore optimizing the effectiveness of activity recording. Electrodes were also arranged to be aligned with the microfluidic chambers in order to specifically stimulate axons that were growing between the two compartments. Isolation of the two cell types allows for the selective treatment of neurons or muscle fibers to assess NMJ functionality hallmarks. Altogether, this microfluidic/microstructured/MEA platform allowed mature and functional in vitro hNMJ modelling. We demonstrate that electrical activation of MNs can trigger recordable extracellular muscle action potentials. This study provides evidence for a physiologically relevant model to mimic a hNMJ that will in the future be a powerful tool, more sensitive than calcium imaging, to better understand and characterize NMJs and their disruption in neurodegenerative diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...